Through the intuitive motor animation, to understand the working principle of the motor!
A motor (commonly known as "motor") refers to an electromagnetic device that converts or transmits electricity according to the law of electromagnetic induction. Its main role is to produce the drive torque, as a power source for electrical appliances or various machines.
The main function of the generator is the use of electrical energy into mechanical energy.
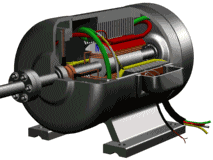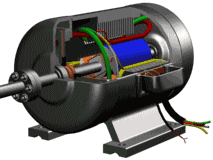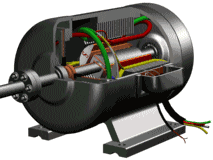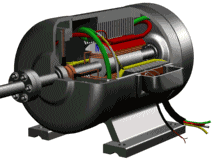
The motor consists essentially of an electromagnet winding or a distributed stator winding and a rotating armature or rotor and other accessories for generating a magnetic field. Under the action of the stator field rotating magnetic field, it has a current in the armature squirrel cage aluminum frame and is rotated by the action of the magnetic field.
Stator (still part)
Stator core: part of the motor magnetic circuit, and placed on the stator winding;
Stator winding: the motor part of the circuit, access to three-phase alternating current, resulting in rotating magnetic field;
Base: fixed stator core and front and rear cover to support the rotor, and from the protection, heat and so on;
Rotor (rotating part)
Rotor core: as part of the motor magnetic circuit and in the core slot placed within the rotor winding;
Rotor winding: cutting stator rotation magnetic field to generate induced electromotive force and current, and the formation of electromagnetic torque to make the motor rotation;
∞
1. a DC motor
▼
A DC motor is a rotating electric machine that converts DC power into mechanical energy (DC motor) or converts mechanical energy into DC power (DC generator). It is able to achieve the DC power and mechanical energy conversion of the motor.
When it is a motor motor is a DC motor, the electrical energy into mechanical energy; for the generator is a DC generator, the mechanical energy into electrical energy.
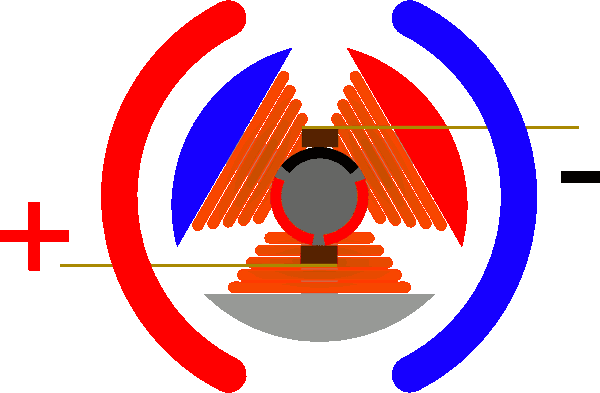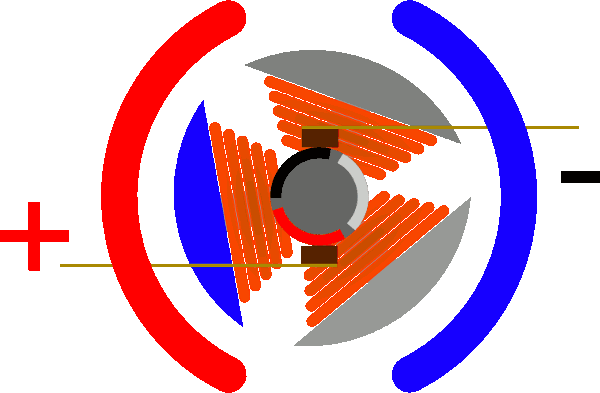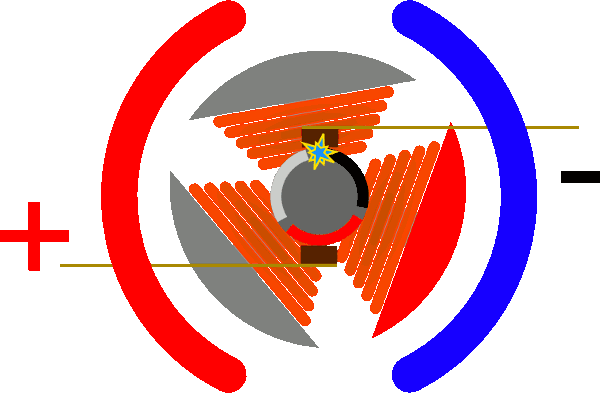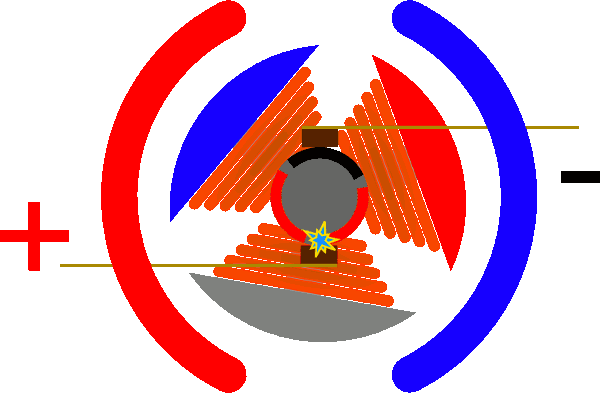
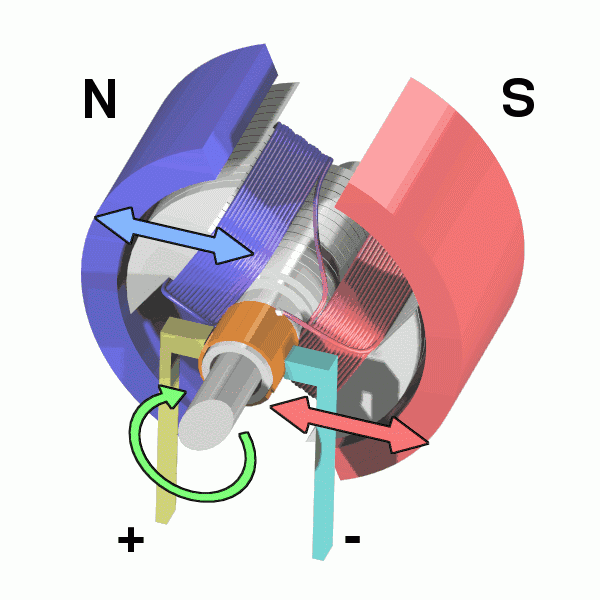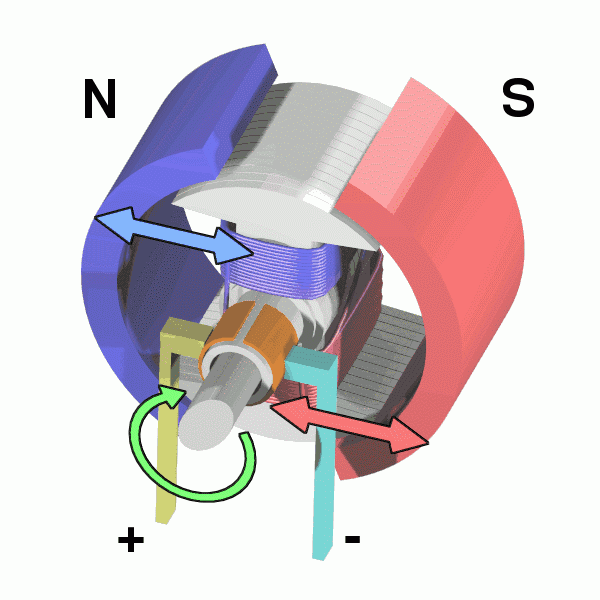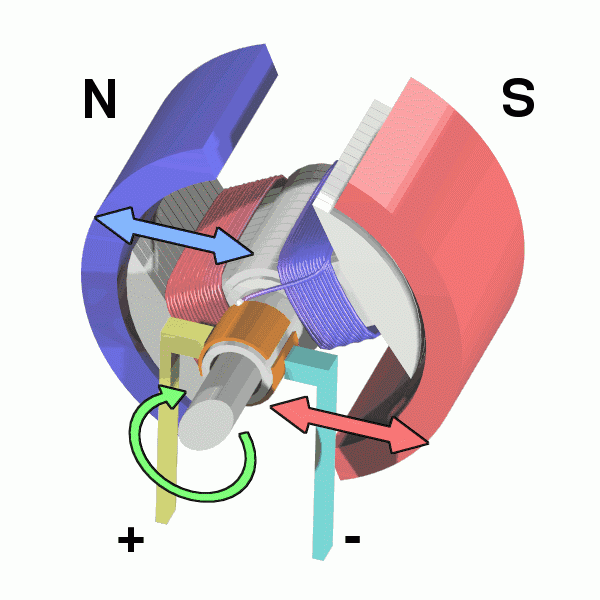
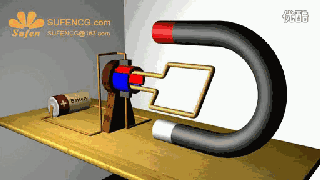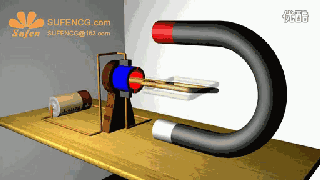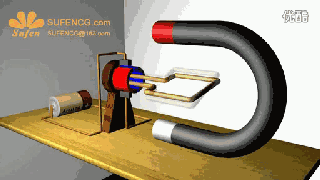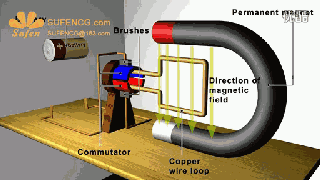
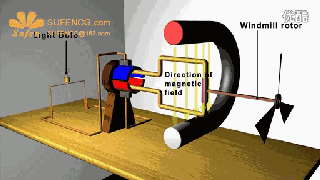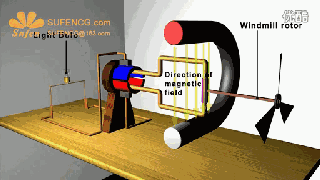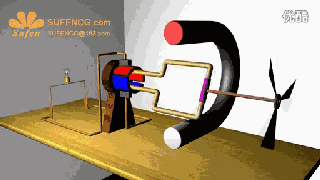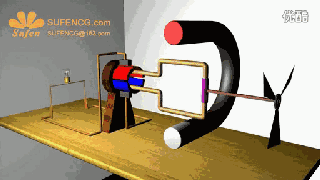
The physical model of DC motor

The figure above shows the physical model of the DC motor, the fixed part of the magnet, here called the main pole; fixed part of the brush. The rotating section has a toroidal core and a winding wound around the toroidal core. (Where two small circles are provided to facilitate the representation of the conductor potential or the direction of the current at that position)
∞
Stepper motor
▼
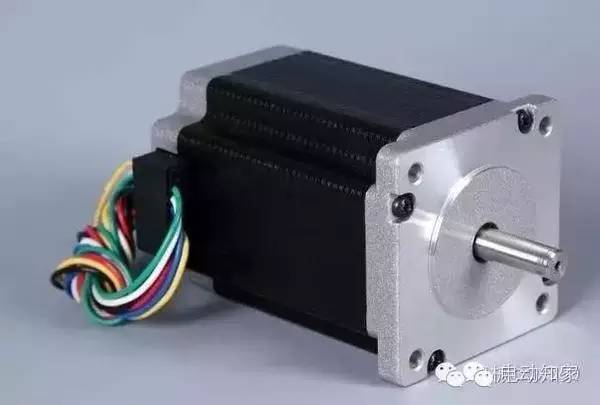

The stepper motor is an open-loop control element stepper motor that converts an electrical pulse signal into angular displacement or line displacement.
In the case of non-overload, the speed of the motor, the stop position depends only on the frequency and the number of pulses of the pulse signal, and is not affected by the load change. When the stepping driver receives a pulse signal, it drives the stepper motor Set the direction of rotation to a fixed angle.
Can control the number of pulses to control the angular displacement, so as to achieve the purpose of accurate positioning; at the same time by controlling the pulse frequency to control the motor speed and acceleration, so as to achieve the purpose of speed.

Stepping motor works
▼
When the current flows through the stator windings, the stator windings produce a vector magnetic field. The magnetic field will drive the rotor to rotate at an angle so that the direction of the pair of magnetic fields of the rotor coincides with the direction of the magnetic field of the stator.
When the stator's vector magnetic field rotates an angle. The rotor also rotates with the magnetic field at an angle. Each time an electric pulse is input, the motor rotates one angle forward.
The angular displacement of the output is proportional to the number of pulses entered and the speed is proportional to the pulse frequency. Change the order of the winding power, the motor will reverse. It is possible to control the rotation of the stepping motor by the number of control pulses, the frequency and the energization sequence of each phase winding of the motor.
∞
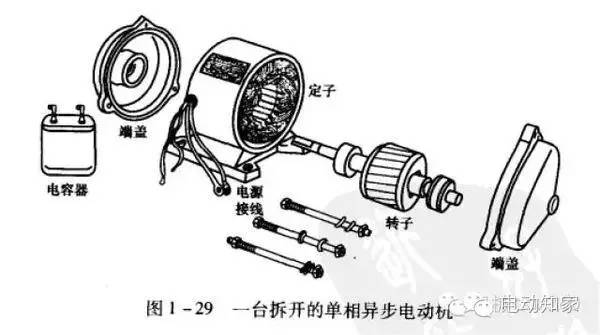
3. One-way asynchronous motor
▼
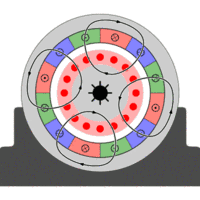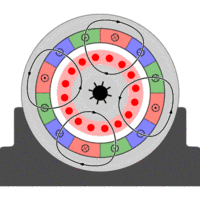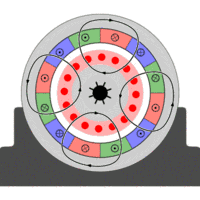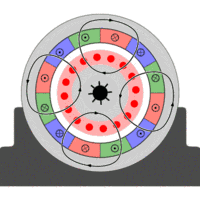
Asynchronous motor, also known as induction motor, is composed of air gap rotating magnetic field and the rotor winding induced current interaction to produce electromagnetic torque, in order to achieve mechanical and electrical energy conversion to mechanical energy of an AC motor.
The working principle of single - phase asynchronous motor
▼
In the AC motor, when the stator winding through the AC current, the establishment of the armature magnetomotive force, which the motor energy conversion and performance have a great impact.
So the single-phase AC winding into the single-phase AC pulse generated magnetic potential, the magnetic potential can be decomposed into two equal amplitude, the opposite rotation of the rotational magnetomotive force, and thus in the air gap to establish positive and reverse Magnetic field and.
The two rotating magnetic fields cut the rotor conductors and generate induced electromotive forces and induced currents respectively in the rotor conductors.
The current interacts with the magnetic field to produce positive and negative electromagnetic torques. The forward electromagnetic torque attempts to turn the rotor forward; the reverse electromagnetic torque attempts to reverse the rotor. The two torques are superimposed to push the rotation of the motor.
∞
4.Permanent magnet motor
▼
The permanent magnet motor is a motor that uses a permanent magnet to provide a magnetic field. Motor work, need two conditions, one exists magnetic field, the other is a magnetic field exists in the movement of the current.
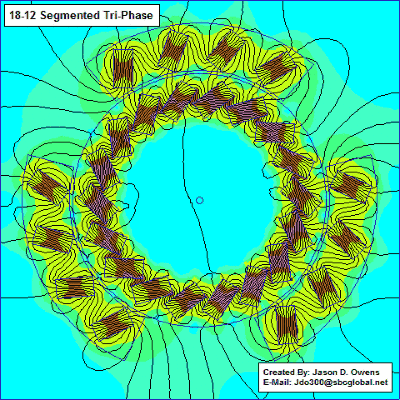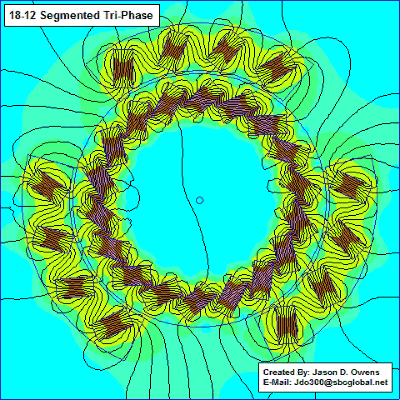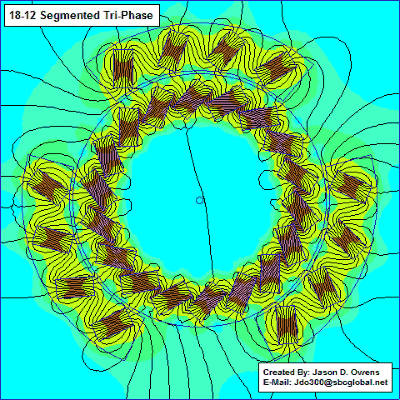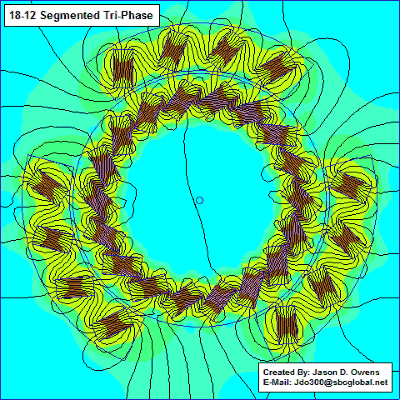
The motor section shows how it works
▼
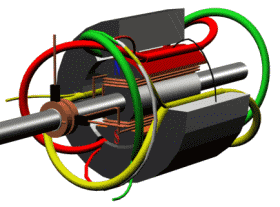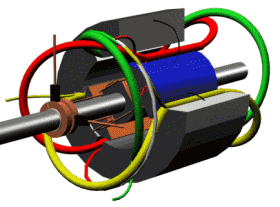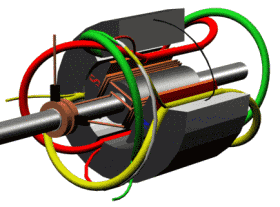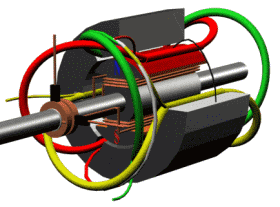













 RCCN WeChat QrCode
RCCN WeChat QrCode Mobile WebSite
Mobile WebSite